We are living in an era of digital transformation and technology disruptions in almost all the walks of life. With the smart phone revolution, we are experiencing dramatic changes in the mobility arena. Mobile apps are getting released every day, changing the way we do business and transforming Customer Experience. The approach to Mobile application development differs largely from the desktop application development because of the fundamental low memory foot print and single user centric nature of the mobile platform. In this highly competitive scenario, the differentiator lies in leveraging the development approach tactically easier, faster and hence faster GTM (Go-To-Market) with a highly optimized performance.
Developing an application on a mobile platform is not a heavy task now days. The platform itself provides the SDK and it will expose the features pertaining to the API. Well explanatory documentation along with sample/code snippets makes the job easy too. By knowing how to assemble the code structure with respect to that particular platform and by following the life cycle of the SDK, we can definitely make an application.
In traditional approach of developing an application on any mobile platform (be it on android/iOS/windows) the focus is to get onto the screen based development approach. You have got an application to develop and customer has provided the use cases. Quickly, business analyst’s defines the use cases and transforms those use cases into screens. The next phase is the development of the application. If a project has got 3 developers assigned, project manager quickly assigns the screens to individual developers where every individual developer starts developing his or her own assigned areas. Each developer makes their presentation layer to the controller to model layer till the data end points. The code gets merged, the application is done and it goes to build.
What we will achieve?
- Tightly Coupled code all around
- Duplicate code throughout the application
- Largely unstructured code
- Unreleased Resources
What are the challenges?
- Problem in Unit Testing
- Unaccounted increase in effort while modification of features or data point and patchy code
- Performance issues due to unwanted memory leakage
- Maintenance issues – huge line of a stub. More than recommended line of code per stub and hence per classes
- Build – test cycle increases
- Delivery goes over run
These are some of the serious challenges that cannot be overlooked in the case of mobile application development.
In this age of digital transformation using disruptive technologies, the approach to mobile app development is experiencing a sea of changes.
How we can make this better.
Pic: Dissection
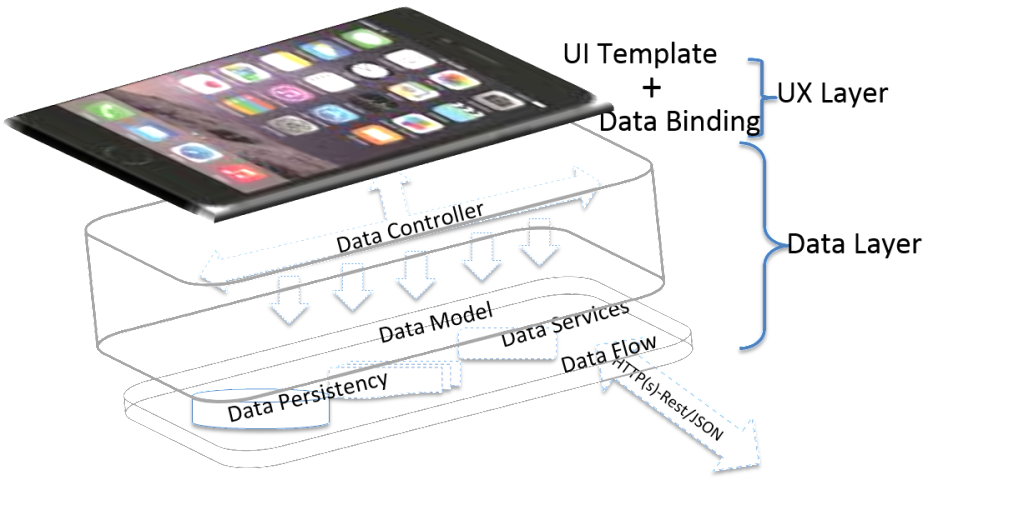
An application is a composite of screens to deliver certain objectives collectively. This collection of screens is nothing but the presentation layer. One part of it to make the layout structuring in xml or storyboard and data binding.
Underneath of the presentation layer of an application is all about data. It is like pathways or nervous system. If paths/roads are not proper, traffic clogging is evident. Therefore laying of proper path ways, helps to improve those impediments. That means the response time at the UX level (at the presentation layer) is dependent on response data from these layers. How fast my data can travel without having tangled. These are the foundation of any application to be robust, scalable and maintainable.
We can follow any design pattern, mostly MVC or MVVC is followed in mobile application development to segregate the layers. But irrespective to that, code gets very tightly coupled to the view layer, at the service layer or at the persistent layer because of the tightly bound data dependencies to the object. Once the same data structure gets little bit modified and connected all views, the service layer need to be modified. This is a major pain point which percolate as a daemon in the complete application code base.
Therefore, dependency injection is very useful to resolve this kind of tightly coupling. It helps to reduce the code and maintainability will be easy. Dependency injection is possible at the data binding, listeners as well as at the service layer. The dependency injection libraries that are currently available are largely static in nature and it resolves at the compilation time rather than at the run time. Therefore the overhead of reflection burdened to runtime maturity is none. So far SDK did not imbibe any kind of injection facility. But once it is matured enough it would be taken at the SDK level.
In mobile applications, the data will be disconnected unless it is received via WIFI or 2G/2.5G/3G/4G. Data can also be persistent at a local data store at SQLite3 and to connect to the server, data transmission via internet is inevitable. This gets resolve via REST services over HTTP(s). Data can be encapsulated either via JSON/XML structure. If an application is not static in nature almost all application requires to have REST service call to the web server. Therefore, the REST API call and data conversion are required for all applications. Likewise, there are several such generic functionalities, which we can depend on already build up dedicated libraries. Use of matured library would help to avoid cluttered code and effective data transmission at the each data Mapping and Junction points like ORM, Sync/Async HTTP handler etc.
Use of efficient communication message queue in the form of pub-sub design model (away from observer or factory pattern) is required to make separation of data point and to have clean entries and exits.
Another relief is in generic form and looking for repeatable usage of particular use case and making a component. The major advantages of usage of the component are that it reduces repeatable coding, define contract of input/expected output in a better way and the code will be less prone to errors. Therefore, the building of component having repeated outcomes, for example, image downloader, pdf generator, dynamic template builder etc. would complement a clean design.
Therefore in a nutshell, efficient app development approach in mobility should categorize the overall application in terms principle design pattern and complement with other matured libraries(Dependency Injection, Sync/Async Rest API handler, Logger, crash analytics, and exception etc.) along with a dedicated component. Anyhow libraries, component, UI template would complement for a faster and clean development. However, separately they are headless in an application unless we tie and give it a form. Last but not the least, to bind these Template UI, libraries, Component and a specific structure (an encapsulation) is essential in the form of an Application Framework. This will help all the project to start as a booster, and not necessarily from the scratch.

Subir Roy has 14+ years of experience in architecting, developing and delivering solutions for different industries. Subir is an expert in understanding systems, and analyzing gaps in mobility platforms. He is the advanced mobility lead at Happiest Minds.